

Understanding ESA Federal Law: Your Guide to Rights and Responsibilities
by Lena Park
Last updated: July 11, 2025
Verified and Approved by:
Angela Morris,
MSW, LCSW
Fact Checked

Overview
This article seeks to illuminate the rights and responsibilities associated with Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) under federal law, recognizing the emotional struggles many individuals face.
While ESAs offer vital emotional support, as acknowledged by the Fair Housing Act, it’s important to understand that they do not possess the same public access rights as service animals. This distinction can be confusing and may lead to feelings of uncertainty for ESA owners.
Therefore, it is crucial for individuals to be aware of their legal protections and obligations in various contexts, ensuring they feel supported and informed as they navigate these complexities.
Introduction
Understanding the legal landscape surrounding Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) is essential for individuals seeking comfort and companionship through these unique pets. Many people face emotional challenges that can feel overwhelming, and the presence of an ESA can offer much-needed solace.
As the recognition of ESAs grows, so does the need for clarity regarding the rights and responsibilities that accompany their ownership. What happens when the laws governing these animals intersect with housing and travel regulations? It can be daunting to navigate these complexities, especially when all you want is to ensure your emotional well-being.
However, there is hope. By understanding the legal protections available and how to obtain an ESA letter, you can take meaningful steps toward securing the support you deserve.
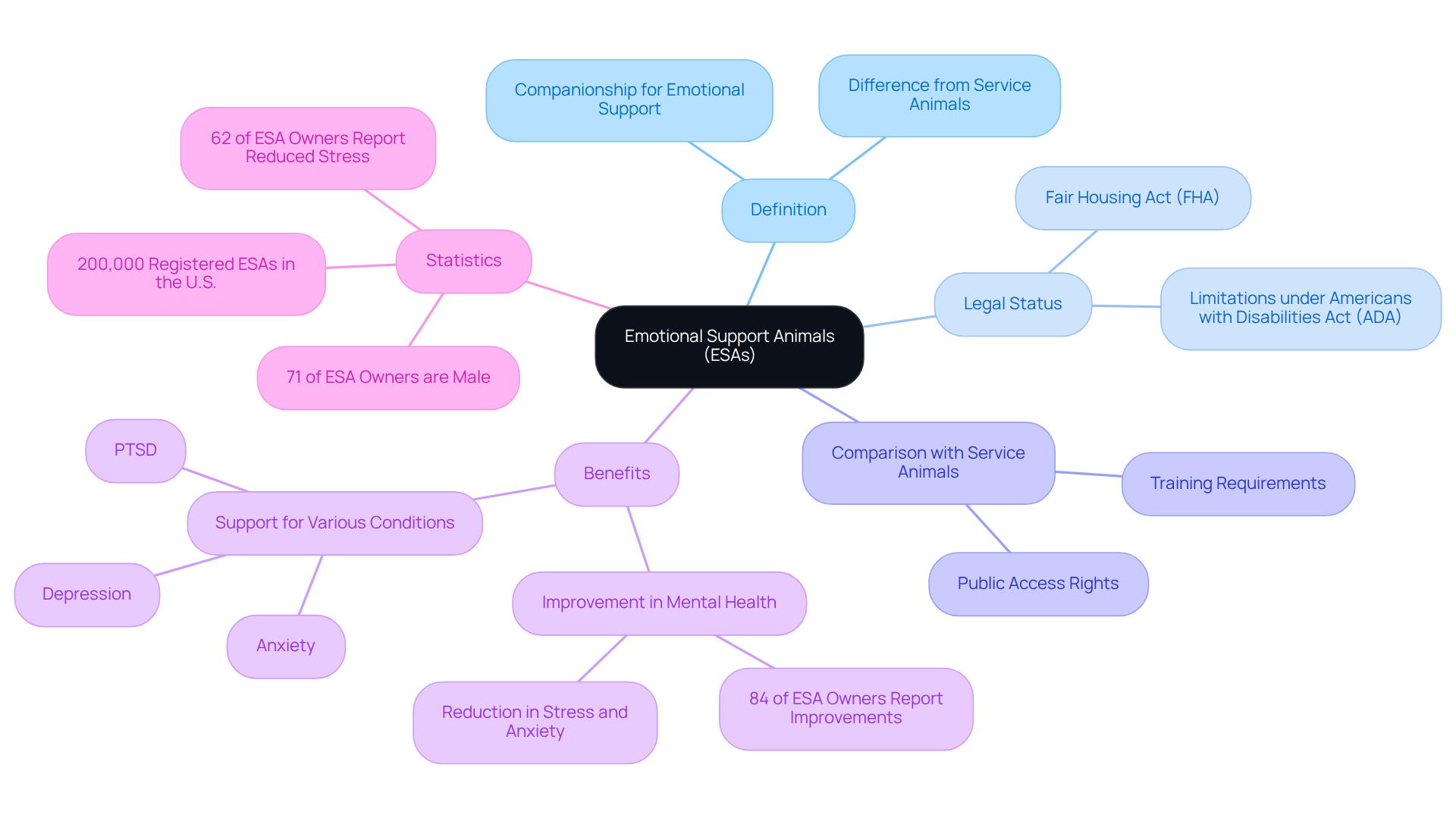
Define Emotional Support Animals and Their Legal Status
Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) offer essential companionship to those grappling with emotional or psychological challenges, providing comfort and assistance without the need for specialized training. Many individuals face significant emotional struggles, such as anxiety, depression, and PTSD, and the presence of an ESA can be a source of solace. Unlike service animals, which are trained to perform specific tasks for those with disabilities, ESAs primarily focus on alleviating the symptoms associated with these mental health conditions through companionship.
Legally, under ESA federal law, ESAs are recognized by the Fair Housing Act (FHA), which allows individuals to reside with their animals in housing that may otherwise restrict pets. This legal framework, governed by ESA federal law, is vital for ESA owners, helping them navigate housing situations that could pose challenges due to pet restrictions. However, it’s essential to understand that emotional support animals do not have the same public access rights as service animals under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Service dogs are trained to perform specific tasks and enjoy complete public access rights, allowing them to accompany their owners in all public areas. This distinction highlights the importance for ESA owners to be informed about their rights and limitations in various environments.
As of 2023, there are approximately 200,000 registered ESAs in the U.S., reflecting a growing recognition of their role in supporting mental well-being. Recent studies indicate that 84% of ESA owners experience noticeable improvements in their mental health, showcasing the profound impact these animals can have on emotional wellness. Understanding these legal nuances and the evolving landscape of ESA federal law is crucial for individuals seeking the therapeutic benefits of pet companionship.
Have you ever considered how a furry friend might change your life? Comprehending the support available through ESAs can empower you on your journey toward emotional healing.
Explore Federal Laws Governing Emotional Support Animals
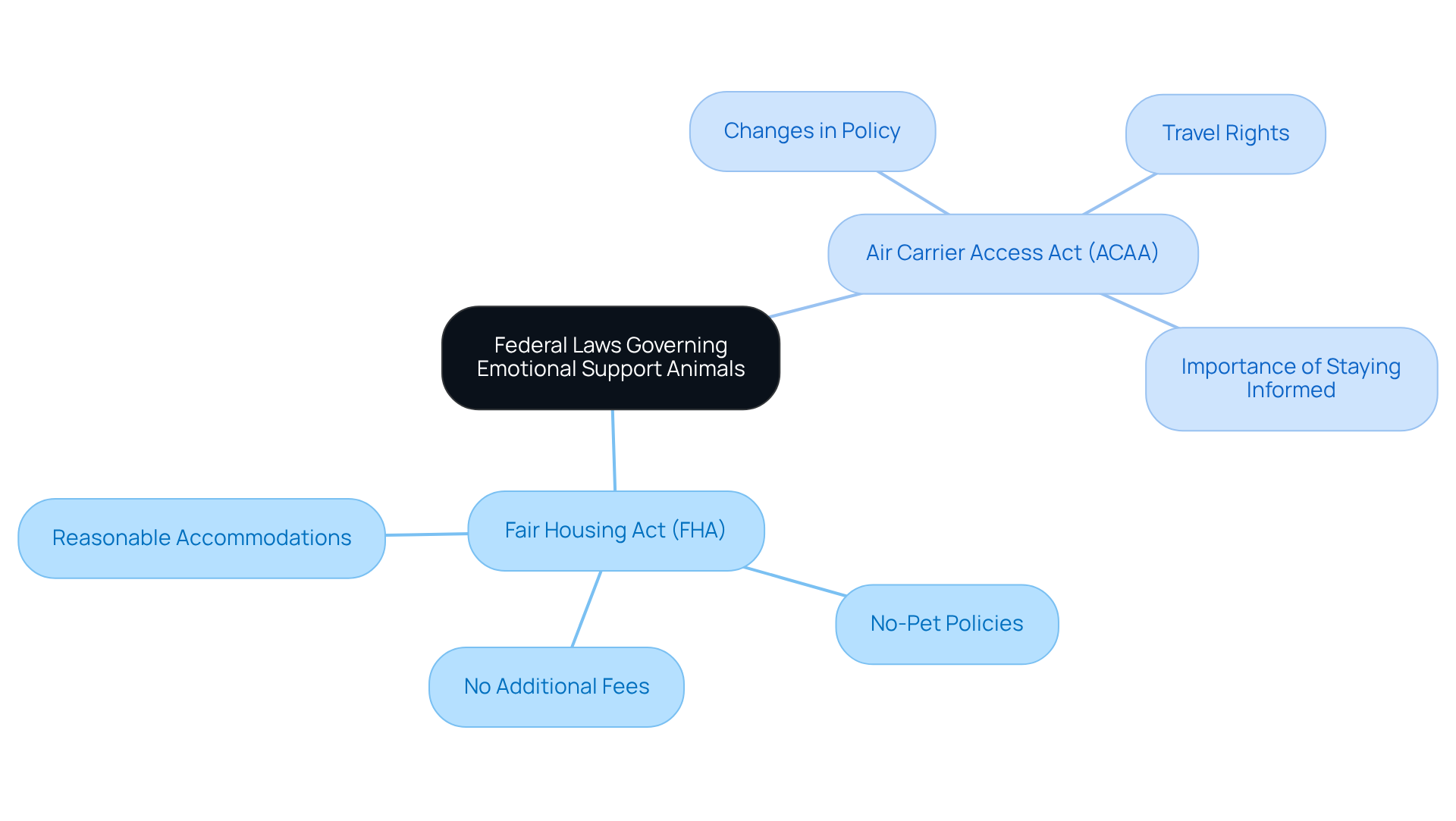
The Fair Housing Act (FHA) stands as a vital federal law that supports individuals with ESAs, or Emotional Support Animals. It requires housing providers to make reasonable accommodations, even in properties that enforce no-pet policies. This important legislation ensures that landlords cannot deny housing solely based on the presence of an ESA, nor can they impose additional fees or deposits related to the pet.
However, the Air Carrier Access Act (ACAA) has seen significant changes that have impacted the rights of ESA owners when it comes to air travel. In the past, ESAs were allowed to accompany their owners on flights, but recent amendments have altered this policy. As a result, ESA owners must stay informed about current regulations to navigate these challenges effectively.
Understanding these laws is crucial, as it empowers ESA owners to advocate for their rights and secure necessary accommodations. Advocacy efforts have underscored the significance of these protections, demonstrating that individuals can successfully address legal challenges and protect their rights under ESA federal law.
Outline the Process for Obtaining an ESA Letter
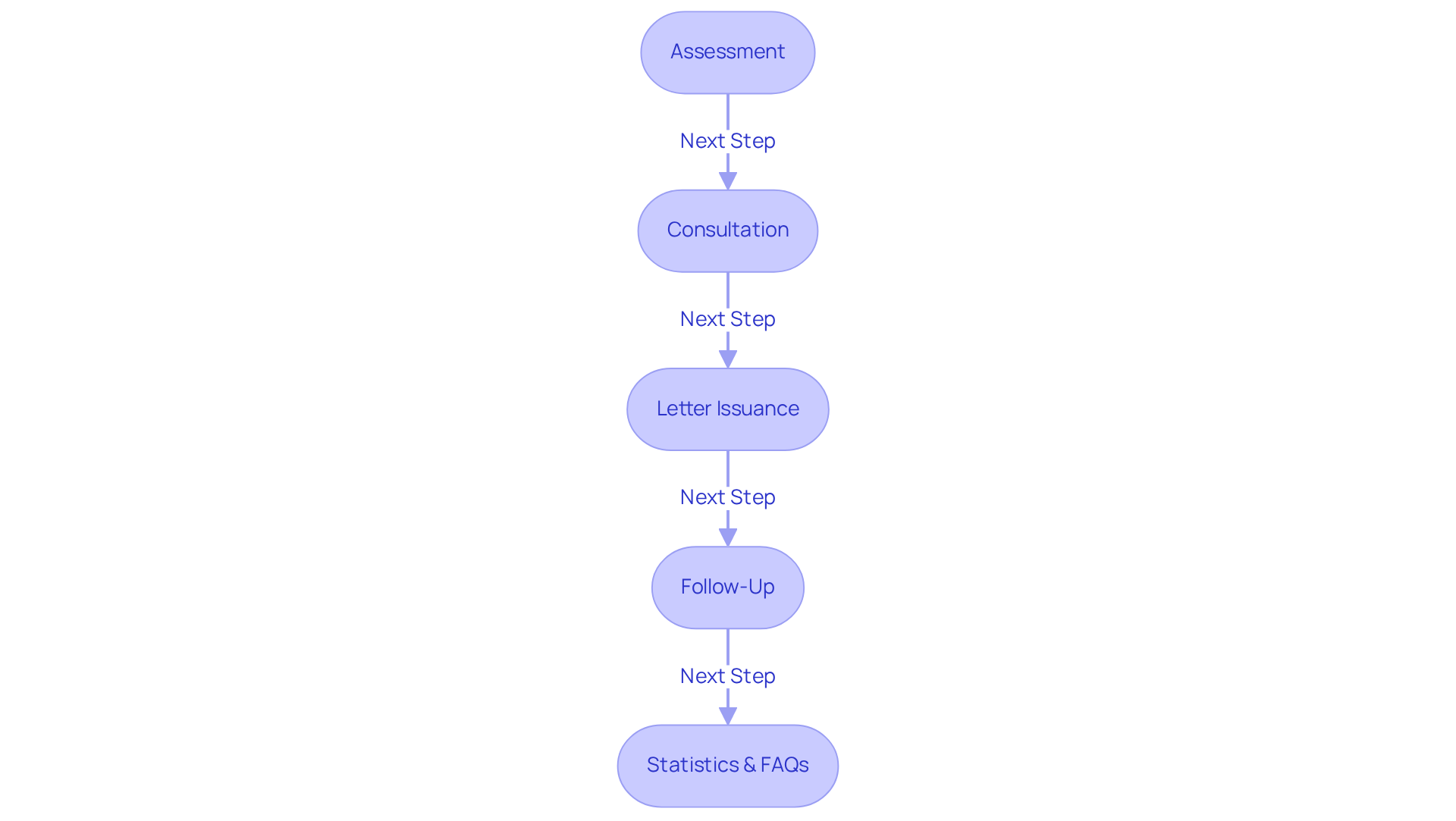
Acquiring an ESA letter involves a thoughtful process designed to ensure individuals receive the essential support for their mental well-being needs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this journey:
- Assessment: Start with a brief assessment to explore your eligibility. This typically includes answering questions about your emotional health and how an Emotional Support Animal (ESA) could positively impact your life.
- Consultation: Schedule a consultation with a licensed mental wellness professional (LMHP). During this meeting, the LMHP will evaluate your mental health needs and discuss the potential benefits of having an ESA. It’s important to note that some states may require a minimum treatment duration before issuing an ESA letter, highlighting the significance of establishing a strong therapeutic relationship.
- Letter Issuance: If approved, the LMHP will provide you with an ESA letter. This document must be printed on official letterhead and include the provider’s licensing details. It serves as vital documentation for housing and travel accommodations, empowering you to advocate for your rights under ESA federal law, as well as the Fair Housing Act and Air Carrier Access Act. In accordance with the ESA federal law, charges for pet rent or other pet-related costs are waived for emotional support animals, providing financial relief for ESA owners.
- Follow-Up: It’s essential to maintain an ongoing relationship with your LMHP. Regular follow-ups are crucial, as some states may require updated letters annually or after a certain duration of treatment. This continuous support is vital to ensure that your ESA continues to meet your mental well-being needs.
Statistics reveal that approximately 200,000 recorded emotional support animals exist in the U.S., with 18% of pet owners identifying their pets as such. While the process for acquiring an ESA letter may vary, many individuals report significant improvements in their daily functioning and mental well-being after welcoming their ESAs into their lives. Mental wellness experts emphasize that the primary criterion for an ESA is its ability to provide comfort and support to those with diagnosed psychological or emotional disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- What is an ESA letter? An ESA letter is a document from a licensed mental wellness professional that certifies your need for an emotional support animal.
- Can I take my ESA on a plane? Yes, under the Air Carrier Access Act, you can travel with your ESA, although airlines may have specific requirements.
- Are emotional support animals permitted in university housing? Yes, emotional support animals are allowed in university accommodations to support students with mental wellness needs, ensuring they have equal access to residential life.
Clarify Handler Responsibilities Under ESA Regulations
Handlers of Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) carry specific responsibilities that are crucial in ensuring a peaceful living environment. These responsibilities are not just tasks; they reflect a commitment to the well-being of both the animals and those around them.
- Care and Supervision: It is vital for handlers to provide comprehensive care, which includes feeding, grooming, and regular veterinary check-ups. This dedication helps maintain the health and happiness of their ESA, which in turn supports the handler’s emotional needs.
- Behavior Management: It’s important that ESAs exhibit appropriate behavior and do not pose a threat to others. If an ESA shows signs of disruptive behavior, the handler is obligated to take corrective measures. This not only protects the community but also nurtures the bond between the handler and their animal.
- Documentation: Handlers should keep their ESA letter readily accessible. This letter is essential for presenting to landlords or housing authorities upon request, ensuring compliance with legal requirements. Having this documentation provides peace of mind and reinforces the handler’s rights.
- Respecting Property: Handlers are accountable for any damage caused by their ESA. It is their responsibility to ensure that their animal does not harm property or disturb other residents. By taking these steps, ESA handlers contribute to a harmonious living environment.
By adhering to these responsibilities, ESA handlers not only uphold their rights under ESA federal law but also cultivate positive relationships with landlords and neighbors. This proactive approach creates a supportive atmosphere that reinforces the legitimacy of their need for emotional support, ultimately leading to a more fulfilling life.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) and the federal laws that govern their rights can feel overwhelming for those seeking emotional companionship. This guide aims to clarify the legal framework surrounding ESAs, ensuring that owners are informed about their rights under the Fair Housing Act and the limitations set by the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Many individuals face emotional challenges that can be daunting. ESAs play a significant role in enhancing mental well-being, providing comfort and companionship that positively impacts their owners’ lives. It’s important to understand the distinction between ESAs and service animals, as each category holds specific legal protections and access rights. Moreover, knowing the process of obtaining an ESA letter and the responsibilities that come with it is essential for fostering a harmonious living environment.
Ultimately, grasping ESA federal law empowers individuals to advocate for their rights while emphasizing the importance of responsible ownership. As the recognition of ESAs grows, it becomes increasingly vital for current and prospective ESA owners to remain informed about evolving regulations and best practices. Embracing this knowledge not only fosters a supportive community but also highlights the therapeutic benefits of emotional support animals, paving the way for a more fulfilling and emotionally healthy life. Remember, you are not alone on this journey; support is available, and understanding your rights can lead to a brighter path ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Emotional Support Animals (ESAs)?
Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) provide companionship to individuals facing emotional or psychological challenges, helping to alleviate symptoms associated with conditions like anxiety, depression, and PTSD without requiring specialized training.
How do ESAs differ from service animals?
Unlike service animals, which are trained to perform specific tasks for individuals with disabilities, ESAs primarily focus on providing comfort and companionship to help manage emotional struggles.
What is the legal status of ESAs under federal law?
ESAs are recognized under the Fair Housing Act (FHA), which allows individuals to live with their animals in housing that may otherwise have pet restrictions. However, ESAs do not have the same public access rights as service animals under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
Do ESAs have public access rights?
No, ESAs do not have the same public access rights as service animals. While service dogs can accompany their owners in all public areas, ESAs are limited in their access to public spaces.
How many registered ESAs are there in the U.S. as of 2023?
As of 2023, there are approximately 200,000 registered ESAs in the U.S., indicating a growing recognition of their role in supporting mental well-being.
What impact do ESAs have on mental health?
Recent studies show that 84% of ESA owners experience noticeable improvements in their mental health, highlighting the significant positive effects these animals can have on emotional wellness.
Why is it important for ESA owners to understand their rights and limitations?
Understanding their rights and limitations helps ESA owners navigate housing situations and public spaces effectively, ensuring they are aware of the legal protections and restrictions that apply to them.
Certify Your Emotional Support Animal Today

Why You Can Rely on Us?
At Wellness Wag, we believe your pet deserves care rooted in both science and compassion. Each article is carefully researched, written in clear language for pet owners, and then reviewed by qualified professionals to ensure the information is evidence-based, current, and practical for real-life care. Our goal is to help you feel confident in making informed decisions about your pet’s health and well-being.
Reviewed by
Angela Morris, MSW, LCSW
Angela is a licensed clinical social worker with 20 years of experience in patient advocacy and community mental health. She has assisted numerous clients with ESA evaluations and brings a deep understanding of disability accommodations, ensuring that all information is accurate, supportive, and practical.

Written by :
Lena Park
Last Updated :
July 11, 2025












