

Master Federal ESA Law: Your Guide to Rights and Responsibilities
by Lena Park
Last updated: July 11, 2025
Verified and Approved by:
Angela Morris,
MSW, LCSW
Fact Checked

Overview
This article highlights the rights and responsibilities of individuals with Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) under federal law. It particularly emphasizes the protections provided by the Fair Housing Act (FHA) and the Air Carrier Access Act (ACAA).
For many, the journey with mental health challenges can feel overwhelming, and having an ESA can provide essential support. While ESA owners enjoy specific legal rights, such as the ability to live with their animals in pet-restricted housing, it is crucial to recognize that these rights come with responsibilities.
Owners must ensure their ESA does not cause damage or disturbances. This balance between rights and obligations is vital in the context of ESA ownership, fostering a harmonious environment for all. By understanding these dynamics, individuals can navigate their experiences with compassion and care, knowing that support is available to help them along the way.
Introduction
Understanding the intricate landscape of Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) is vital for individuals yearning for the comfort and companionship these beloved animals offer.
As the recognition of ESAs expands, so too does the need for clarity about the rights and responsibilities that come with their ownership.
This article explores the federal laws that protect ESA guardians, shedding light on the legal framework that enables them to coexist with their support animals in various environments.
Yet, navigating these regulations can be daunting—what occurs when landlords impose restrictions, or airlines alter their policies?
By delving into these questions, we aim to empower ESA owners to advocate for their rights effectively, ensuring they receive the support they truly need.
Define Emotional Support Animals and Their Legal Status
An Emotional Support Animal (ESA) provides vital emotional, cognitive, or similar support to individuals with disabilities, helping them manage their symptoms. Unlike service animals, ESAs do not require specialized training for specific tasks; however, they must be prescribed by a licensed mental health professional. The Fair Housing Act (FHA) legally recognizes ESAs under federal esa law, allowing individuals with disabilities to live with their ESAs in housing that may otherwise restrict pets. Importantly, there is no requirement for ESAs to be registered or certified, distinguishing them from service animals.
Many individuals face emotional challenges that can feel overwhelming at times. Recent statistics show that approximately 32% of pet caregivers have certified their pets as ESAs, reflecting a growing awareness of their therapeutic benefits. Furthermore, 84% of ESA guardians report significant improvements in their mental health, highlighting the essential role these animals play in enhancing emotional well-being. The federal esa law protects the rights of ESA owners, ensuring they can reside with their companions in pet-restricted accommodations, thus facilitating access to the necessary support for those navigating mental health challenges.
At Wellness Wag, we understand the importance of having the right support. We simplify the process of acquiring valid ESA documents through our telehealth services, offering fast turnaround times and equipping individuals with the knowledge and resources needed to navigate their journey with confidence. We issue ESA letters within 24 hours of approval, ensuring that you have the support you need when you need it most. If you have questions or concerns about this process, we invite you to refer to our FAQs or contact us directly. Your well-being is our priority, and we are here to help you every step of the way.
Explore Federal Laws Impacting ESA Rights
The Fair Housing Act (FHA) serves as a crucial federal esa law that protects the rights of Emotional Support Animal (ESA) guardians. It requires landlords to provide reasonable accommodations for tenants with ESAs, even in properties that have no-pet policies. This federal esa law is designed to prevent discrimination based on disability, ensuring that caregivers of ESAs are exempt from pet fees and breed restrictions. For example, once an animal is verified as an emotional support animal, landlords cannot deny it based on its breed or size. This allows individuals to live in pet-restricted accommodations without incurring additional charges, alleviating some of the stress associated with housing challenges.
In addition to housing rights, the Air Carrier Access Act (ACAA) provides specific protections for ESA handlers during air travel. However, recent changes have tightened these protections, with many airlines now treating ESAs similarly to regular pets. This shift may involve fees and additional documentation requirements. For instance, airlines might ask for a statement from a licensed mental health professional that confirms the necessity of the ESA for travel, alongside a declaration of the passenger’s mental or emotional disability.
Understanding these regulations is vital for ESA custodians to advocate effectively for their rights. Open communication with landlords and airlines, coupled with proper documentation, can significantly improve the chances of securing essential accommodations. Real-life stories illustrate the importance of these regulations: many ESA guardians have successfully navigated housing challenges by presenting valid ESA documents, ensuring their right to live with their support animals. As the landscape of ESA rights evolves, staying informed about these legal frameworks is crucial for all ESA holders, providing reassurance that support is available.
Navigate the Process of Obtaining an ESA Letter
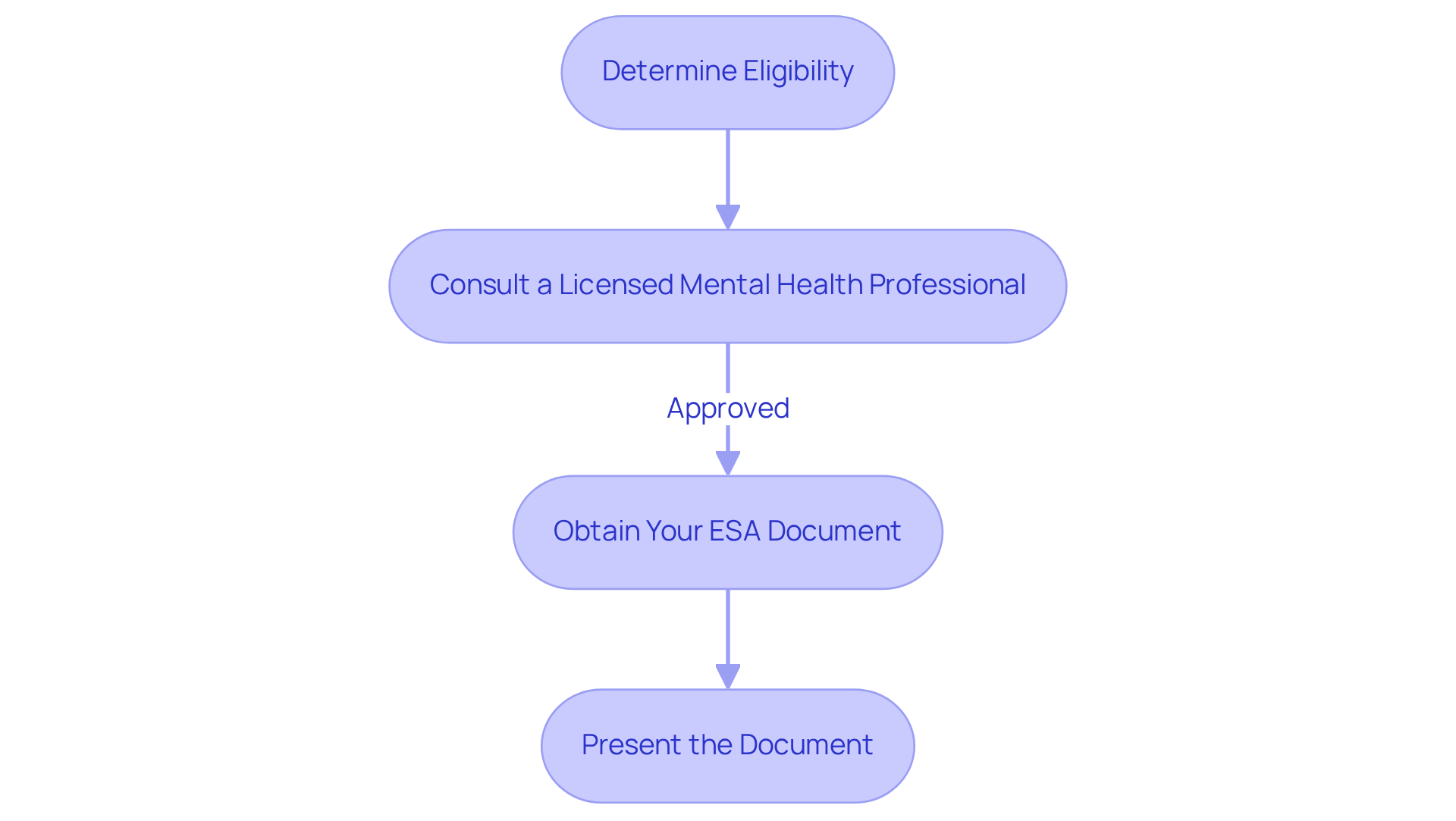
Obtaining an ESA document can feel overwhelming, but by following these essential steps, you can find the support you need.
- Determine Eligibility: Begin by reflecting on whether you have a diagnosed mental health condition that significantly impacts your daily life. It’s important to recognize that around 18% of pet owners in the U.S. have Emotional Support Animals, underscoring the significance of this assessment.
- Consult a Licensed Mental Health Professional (LMHP): Reach out to an LMHP for an appointment to assess your needs and determine if an ESA would be beneficial for you. This professional must establish a meaningful connection with you for at least 30 days before providing documentation, as many states require this for legal compliance. At Wellness Wag, we are here to simplify this process by connecting you with a licensed medical professional for a personalized consultation and thorough evaluation to assess your eligibility for an ESA.
- Obtain Your ESA Document: If you are approved, the LMHP will provide you with an ESA document. This document should include their contact information, license number, and a statement affirming your need for an ESA. It serves as crucial evidence for your rights under the Fair Housing Act and Air Carrier Access Act. Typically, the approval duration for an ESA document is about six weeks, so it’s helpful to be prepared for this timeframe. However, with Wellness Wag, you can look forward to receiving a professionally crafted ESA document with legal recognition within 24 hours of your consultation.
- Present the Document: Use this document to support your entitlements in housing and travel situations, ensuring you are ready to present it when necessary. Remember, ESA letters usually expire after one year, so it’s wise to plan for reassessment to maintain your eligibility.
We understand that this journey can be challenging, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Understand Responsibilities and Rights of ESA Owners
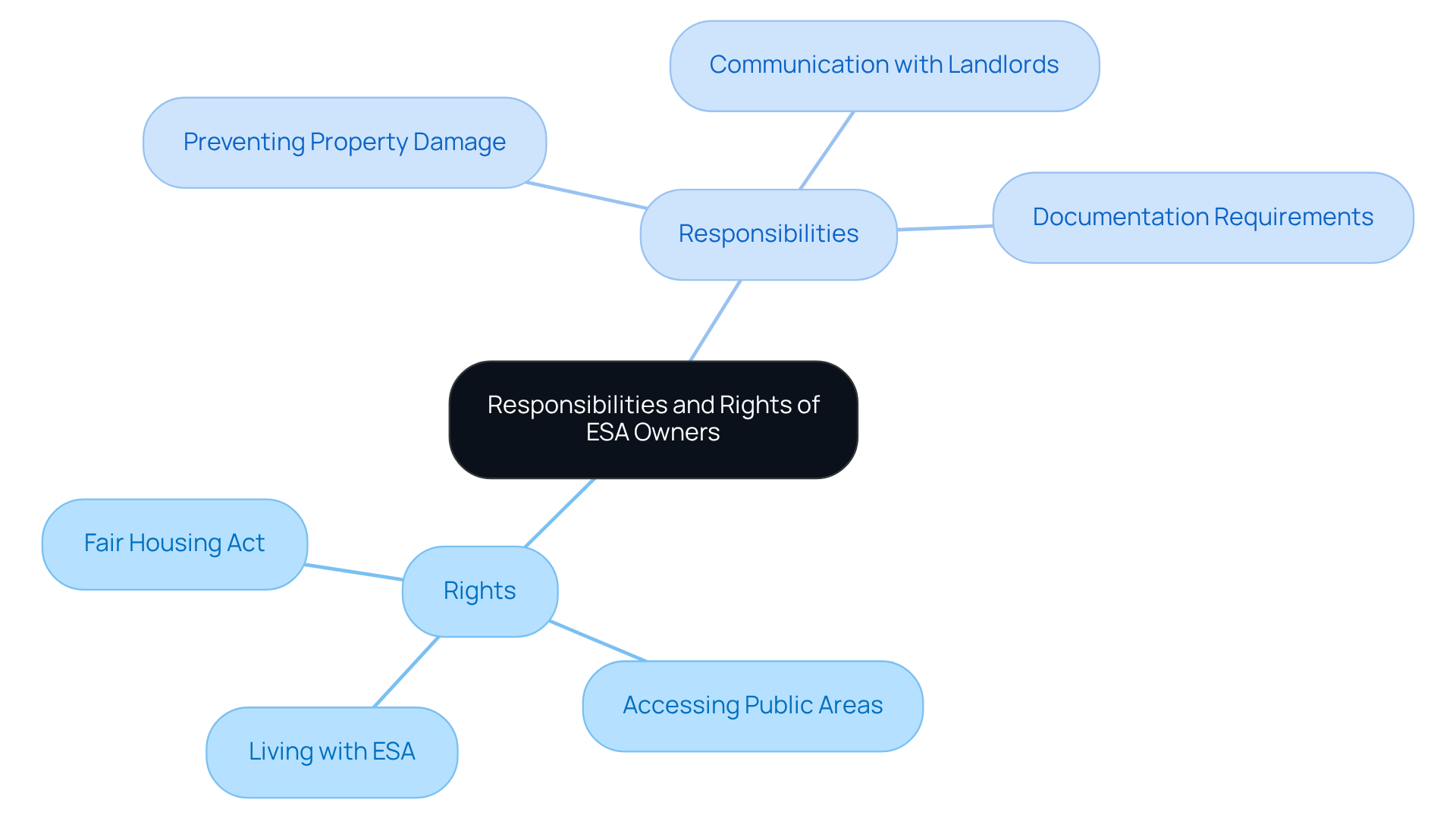
As an ESA owner, you enjoy certain privileges under federal law, including the ability to live with your emotional support animal in housing that typically restricts pets. This important right is reinforced by the Fair Housing Act, which requires reasonable accommodations for individuals with disabilities. In public areas, you also have the ability to access zones with your ESA, provided you have the necessary documentation.
However, with these rights come responsibilities. As an ESA guardian, it’s essential to ensure that your animal does not cause property damage or disturb neighbors. While landlords cannot impose pet fees for ESAs, you may still be held liable for any damages your ESA causes. For example, data indicates that landlords can deduct repair costs from a tenant’s security deposit if an ESA causes damage to the property. One satisfied Wellness Wag client shared a testimonial, highlighting how having proper documentation helped them navigate a challenging housing situation smoothly.
Maintaining open communication with your landlord is vital. Supplying essential documentation, such as a valid ESA letter from a licensed mental health professional, can assist in ensuring adherence to housing regulations. For instance, one ESA owner recounted that presenting their ESA letter upfront led to a positive discussion with their landlord, resulting in a mutually beneficial agreement. Furthermore, while there is no legal requirement for service dogs to be certified or registered, obtaining certification can provide credibility and ensure that the service dog has undergone proper training. Understanding these rights and responsibilities is crucial for navigating the complexities of housing with an ESA.
Conclusion
Understanding the rights and responsibilities associated with Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) is crucial for individuals seeking the comfort and companionship these animals provide. For many, ESAs play a vital role in navigating the emotional challenges of mental health issues. Federal laws, like the Fair Housing Act, ensure that guardians can live with their ESAs in pet-restricted housing, fostering emotional well-being and highlighting the importance of proper documentation and advocacy for ESA owners.
Obtaining an ESA letter can be a vital step towards this supportive relationship. Consulting a licensed mental health professional is essential, as is understanding the legal protections afforded by federal laws. Maintaining open communication with landlords and airlines is also crucial to navigate potential challenges effectively. It’s important to recognize the balance between enjoying the rights granted to ESA owners and fulfilling the responsibilities that come with them, such as preventing property damage and ensuring the animal’s well-being.
In a world where mental health awareness is increasingly recognized, advocating for the rights of ESA owners is more important than ever. Those considering an ESA should take proactive steps to secure their rights and responsibilities, ensuring a harmonious living environment that supports their emotional needs. By staying informed and prepared, individuals can effectively navigate the complexities of ESA ownership and embrace the many benefits these beloved companions provide. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; support is available to help you thrive alongside your emotional support animal.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Emotional Support Animal (ESA)?
An Emotional Support Animal (ESA) provides emotional, cognitive, or similar support to individuals with disabilities, helping them manage their symptoms.
Do ESAs require specialized training?
No, ESAs do not require specialized training for specific tasks, unlike service animals.
Who can prescribe an ESA?
An ESA must be prescribed by a licensed mental health professional.
What legal protections do ESAs have?
The Fair Housing Act (FHA) legally recognizes ESAs under federal law, allowing individuals with disabilities to live with their ESAs in housing that may otherwise restrict pets.
Is there a requirement for ESAs to be registered or certified?
No, there is no requirement for ESAs to be registered or certified, which distinguishes them from service animals.
What percentage of pet caregivers have certified their pets as ESAs?
Approximately 32% of pet caregivers have certified their pets as ESAs.
How do ESAs impact mental health?
About 84% of ESA guardians report significant improvements in their mental health, highlighting the essential role these animals play in enhancing emotional well-being.
How does Wellness Wag assist with acquiring ESA documents?
Wellness Wag simplifies the process of acquiring valid ESA documents through telehealth services, offering fast turnaround times and providing individuals with the necessary knowledge and resources.
How quickly can Wellness Wag issue ESA letters?
Wellness Wag can issue ESA letters within 24 hours of approval.
What should I do if I have questions about the ESA process?
If you have questions or concerns about the ESA process, you can refer to the FAQs on the Wellness Wag website or contact them directly for assistance.
Certify Your Emotional Support Animal Today

Why You Can Rely on Us?
At Wellness Wag, we believe your pet deserves care rooted in both science and compassion. Each article is carefully researched, written in clear language for pet owners, and then reviewed by qualified professionals to ensure the information is evidence-based, current, and practical for real-life care. Our goal is to help you feel confident in making informed decisions about your pet’s health and well-being.
Reviewed by
Angela Morris, MSW, LCSW
Angela is a licensed clinical social worker with 20 years of experience in patient advocacy and community mental health. She has assisted numerous clients with ESA evaluations and brings a deep understanding of disability accommodations, ensuring that all information is accurate, supportive, and practical.

Written by :
Lena Park
Last Updated :
July 11, 2025












