

When Can a Landlord Legally Reject an ESA in Texas?
by Lena Park
Last updated: July 27, 2025
Verified and Approved by:
Angela Morris,
MSW, LCSW
Fact Checked

Overview
For many individuals facing mental health challenges, the journey can often feel isolating and overwhelming. The presence of an Emotional Support Animal (ESA) can provide comfort and companionship during these difficult times. However, it’s important to understand that landlords in Texas can legally reject an ESA request under certain circumstances. This can happen if:
- The animal poses a threat to safety
- The animal is likely to cause property damage
- The animal imposes an undue financial burden
- The tenant fails to provide a valid ESA letter
Recognizing these grounds for rejection is crucial, as it highlights the importance of knowing your rights as a tenant.
Understanding the legal protections available under the Fair Housing Act can help ensure fair treatment for individuals who rely on ESAs. It’s essential to navigate this process with awareness and support. If you find yourself in a situation where your ESA request is challenged, remember that you’re not alone. There are resources and guidance available to help you advocate for your needs and rights, ensuring that you can continue to benefit from the companionship and emotional support your ESA provides.
Introduction
Understanding the complexities surrounding Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) is crucial for both tenants and landlords in Texas. Many individuals face significant emotional challenges, relying on these animals for their well-being. As the number of people seeking comfort from ESAs rises, the legal framework that protects their rights becomes increasingly important.
This article explores the specific circumstances under which a landlord can legally reject an ESA request, while highlighting the essential protections afforded by the Fair Housing Act. However, it is vital to consider what happens when these protections are overlooked or misunderstood.
By exploring the legal landscape, we empower tenants to advocate for their rights and guide landlords in navigating potential pitfalls. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there is support available to help you through these complexities.
Define Emotional Support Animals and Their Legal Protections in Texas
Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) play a vital role in providing comfort and support to individuals grappling with mental health conditions, such as anxiety, depression, or PTSD. In Texas, the Fair Housing Act (FHA) protects the rights of those who need ESAs, ensuring that property owners must allow residents to keep their animals, provided they have a valid ESA letter from a licensed mental health professional. This letter is not just a formality; it validates the tenant’s need for their animal, allowing them to coexist in housing that often restricts pets.
It’s essential to understand that while ESAs offer significant emotional support, they are not classified as service animals under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). This distinction means they do not have the same access rights in public spaces, yet they are still afforded critical protections in housing situations.
Under the FHA, property owners cannot impose pet deposits, monthly pet rent, or additional fees for ESAs. This provision is crucial in ensuring that individuals facing mental health challenges can secure housing without encountering financial obstacles. Recent surveys reveal that approximately 18% of pet owners in the U.S. have Emotional Support Animals, and notably, 62% of ESA owners reported an improvement in their mental health during the pandemic. This statistic underscores the profound impact these animals have on emotional well-being.
It’s also important to recognize that around 70% of pet owners do not have their pets certified as ESAs, often due to a lack of knowledge about the certification process or the belief that they do not qualify.
Understanding when a landlord can legally reject an ESA in Texas is vital for individuals who are navigating housing challenges while ensuring their rights are upheld. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are supportive pathways available to help you maintain a fulfilling life with your ESA by your side.
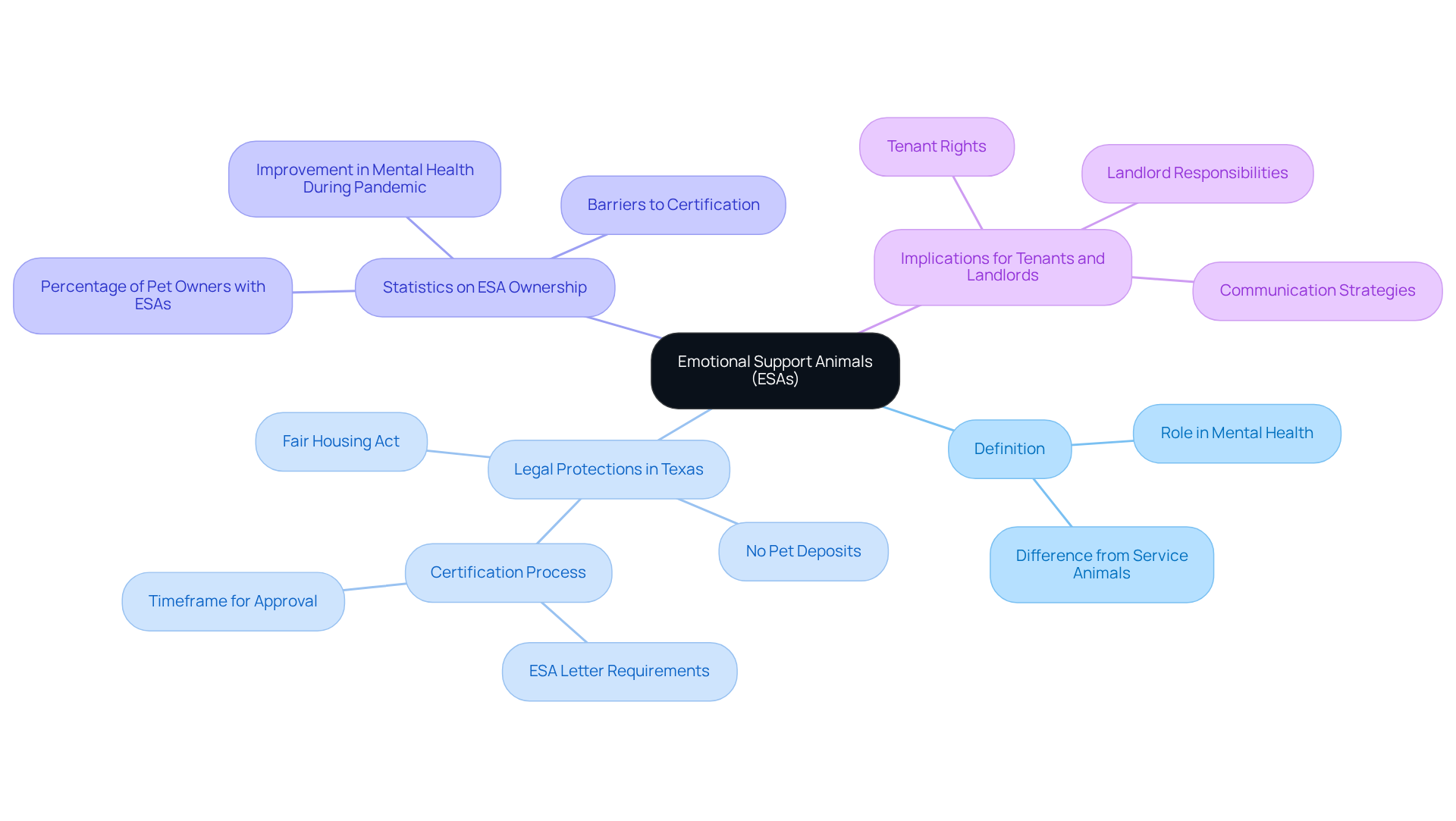
Identify Grounds for Landlord Rejection of an ESA Request
While property owners generally cannot deny an ESA request without valid reasons, it’s essential to understand that specific grounds exist for legal rejection. This can be particularly concerning for individuals who rely on emotional support animals for their well-being.
-
Threat to Safety: If the ESA presents a direct risk to the health or safety of others, property owners may have grounds for denial. This includes situations where the animal exhibits aggressive behavior or poses a risk of injury. It’s heartbreaking to think that an individual’s source of comfort could be viewed in such a light.
-
Property Damage: Landlords can reject ESA requests if there is credible evidence that the animal is likely to cause significant damage to the property. This concern is especially pertinent in situations where former occupants have reported issues with similar animals. The fear of losing a safe space can be overwhelming.
-
Undue Financial Burden: If accommodating the ESA would impose an unreasonable financial burden on the landlord, they may deny the request. However, this is a rare justification and must be well-documented. It’s crucial for both parties to communicate openly about financial concerns.
-
Non-compliance with ESA Requirements: Landlords can deny requests if residents do not submit a valid ESA letter or if the letter does not fulfill regulatory standards. Authentic documentation from a licensed healthcare professional is essential for compliance with the Fair Housing Act. This requirement is vital to ensure that the needs of individuals are respected.
Understanding these reasons is vital for residents as they organize their paperwork and reasoning when pursuing housing for their ESAs. In Texas, property owners must tread carefully to avoid discrimination, as denying an ESA can lead to serious legal repercussions, including discrimination lawsuits. It’s important to remember that 31.0% of residents report interactions with assistance animals, underscoring the significant role ESAs play in residential environments. Furthermore, property owners managing small buildings with four or fewer units are exempt from FHA rules regarding ESAs, which can influence their decision-making process. By being informed about these legal frameworks, renters can better advocate for their rights while property owners can ensure compliance and avoid potential disputes. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and support is available to help you navigate these challenges.
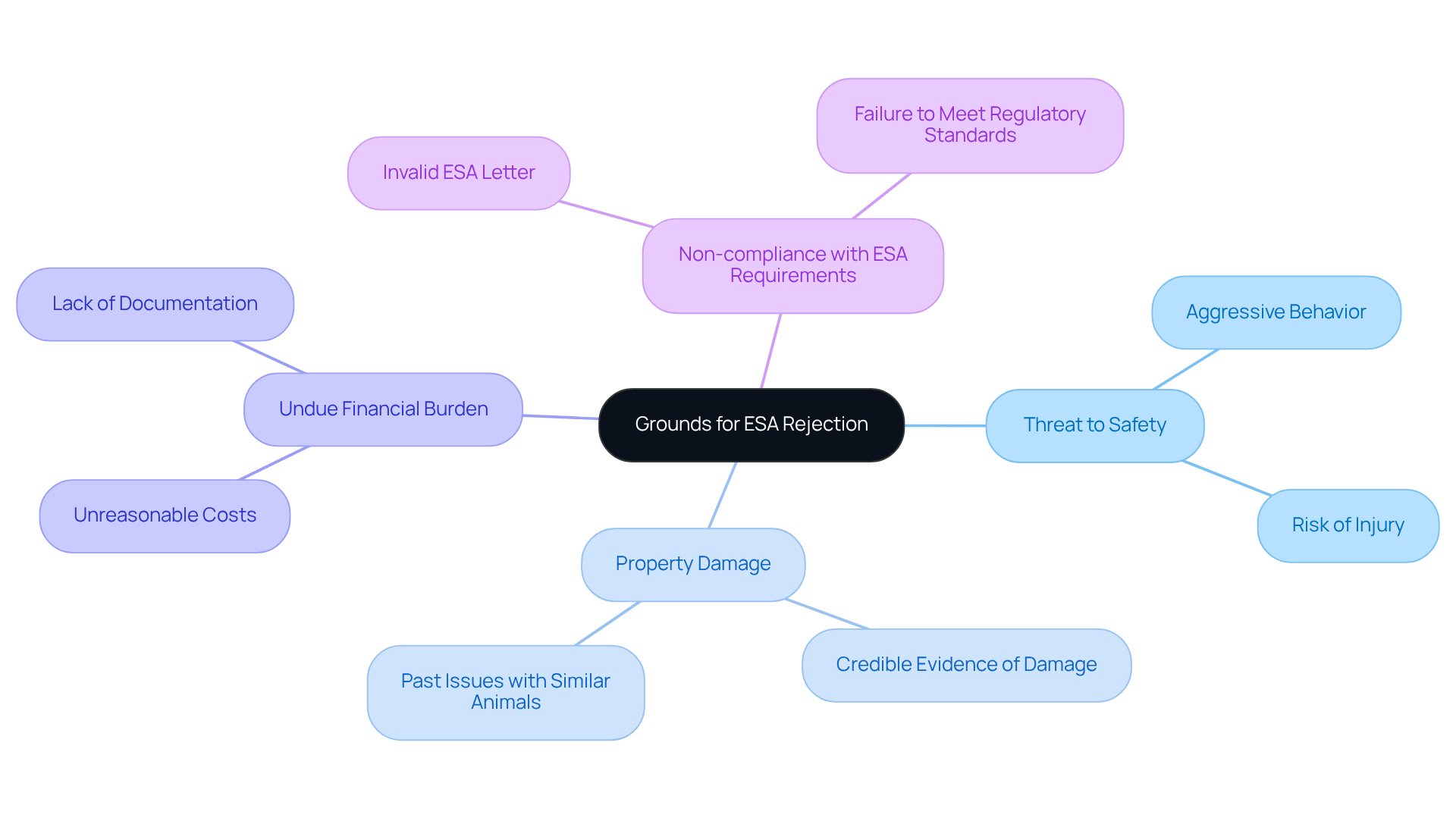
Outline Steps to Challenge an Unjust ESA Denial
It can be disheartening for renters who rely on Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) when considering when can a landlord legally reject an esa in texas. Here are some compassionate steps to contest such a decision:
-
Request Written Denial: Begin by asking the property owner for a written explanation that details the reasons for the denial. This documentation is vital for any further action you may need to take.
-
Review ESA Letter: Ensure that the ESA letter you have is authentic and meets regulatory standards. It should include the licensed mental health professional’s contact details and a clear declaration of your mental health condition. If you notice any discrepancies, reach out to the mental health professional who issued the letter for necessary corrections.
-
Communicate with the Landlord: Open a dialogue with your landlord to address their concerns. Providing additional documentation or clarifications can help alleviate misunderstandings and foster a supportive conversation.
-
Submit a Grievance: If the issue continues, consider submitting a grievance to the Texas Department of Housing and Community Affairs or seeking assistance from a lawyer who specializes in housing law. You deserve to have your rights respected.
-
Consider Mediation: Mediation can be a gentle and effective way to resolve disputes amicably, helping to avoid the stress of judicial action.
-
Judicial Measures: As a last resort, renters may seek judicial measures against the landlord for infringing upon their rights under the Fair Housing Act (FHA). This step should be taken with the guidance of a qualified expert to ensure you are properly represented.
It’s important to recognize that approximately 18% of pet owners in the U.S. have Emotional Support Animals, underscoring the significance of understanding tenants’ rights regarding ESA accommodations. Furthermore, landlords may face legal consequences if they improperly deny ESA requests, raising the question of when can a landlord legally reject an esa in texas, as illustrated by a federal judge’s ruling against a Texas housing provider. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there is support available to help you navigate these challenges.
Conclusion
Emotional Support Animals (ESAs) serve as vital companions for many individuals navigating the challenges of mental health, offering essential support and comfort. In Texas, the legal framework surrounding ESAs is crafted to protect tenants’ rights while also delineating specific circumstances under which landlords may justifiably deny ESA requests. Grasping these nuances is crucial for both renters and property owners, ensuring that the rights and responsibilities of each party are honored.
This article sheds light on important facets of ESA regulations in Texas, including:
- The legal protections afforded under the Fair Housing Act
- The valid grounds for landlords to reject ESA requests
- The steps tenants can take to contest unfair denials
Factors such as safety concerns and non-compliance with documentation requirements significantly influence the landlord-tenant relationship. Moreover, the importance of open dialogue and the potential for mediation are highlighted as constructive avenues for resolving disputes.
Navigating the complexities of ESA regulations in Texas ultimately requires a collective effort. Tenants should be aware of their rights and be ready to advocate for themselves, while landlords are encouraged to handle these requests with sensitivity and compliance with the law. By nurturing understanding and cooperation, both parties can strive towards a housing environment that honors the needs of individuals depending on Emotional Support Animals, ensuring that mental health and well-being remain a priority in residential spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Emotional Support Animal (ESA)?
An Emotional Support Animal (ESA) is an animal that provides comfort and support to individuals dealing with mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, or PTSD.
What legal protections do ESAs have in Texas?
In Texas, the Fair Housing Act (FHA) protects the rights of individuals needing ESAs, requiring property owners to allow residents to keep their animals if they have a valid ESA letter from a licensed mental health professional.
How does an ESA letter function?
The ESA letter validates the tenant’s need for their animal, allowing them to live in housing that typically restricts pets.
Are Emotional Support Animals considered service animals?
No, ESAs are not classified as service animals under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and do not have the same access rights in public spaces.
What restrictions do property owners have regarding ESAs under the FHA?
Property owners cannot impose pet deposits, monthly pet rent, or additional fees for ESAs, ensuring that individuals with mental health challenges can secure housing without financial obstacles.
What percentage of pet owners in the U.S. have ESAs?
Approximately 18% of pet owners in the U.S. have Emotional Support Animals.
What impact do ESAs have on mental health?
Recent surveys indicate that 62% of ESA owners reported an improvement in their mental health during the pandemic, highlighting the significant positive impact these animals can have.
Why do many pet owners not have their pets certified as ESAs?
Around 70% of pet owners do not have their pets certified as ESAs, often due to a lack of knowledge about the certification process or the belief that they do not qualify.
When can a landlord legally reject an ESA in Texas?
It is important for individuals to understand the specific circumstances under which a landlord can legally reject an ESA, as this knowledge is crucial for navigating housing challenges and ensuring their rights are upheld.
Certify Your Emotional Support Animal Today

Why You Can Rely on Us?
At Wellness Wag, we believe your pet deserves care rooted in both science and compassion. Each article is carefully researched, written in clear language for pet owners, and then reviewed by qualified professionals to ensure the information is evidence-based, current, and practical for real-life care. Our goal is to help you feel confident in making informed decisions about your pet’s health and well-being.
Reviewed by
Angela Morris, MSW, LCSW
Angela is a licensed clinical social worker with 20 years of experience in patient advocacy and community mental health. She has assisted numerous clients with ESA evaluations and brings a deep understanding of disability accommodations, ensuring that all information is accurate, supportive, and practical.

Written by :
Lena Park
Last Updated :
July 27, 2025












